Orthodrome
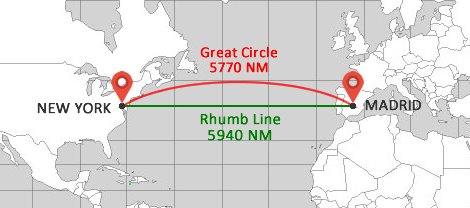
An orthodrome, also known as a great circle route or geodesic line, is the shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere, such as the Earth. It is not a straight line on a two-dimensional map but rather follows the curve of the Earth's surface. Orthodromes are used in navigation, particularly in aviation and maritime travel, where finding the most efficient path between two locations is crucial.
Read MoreOrthodrome Calculator
NavigationTools.it is a specialized website designed to help aviation enthusiasts and pilots master Orthodromes calculations. With educational resources the website aims to empower users in understanding and applying Orthodrome in navigation.
Read More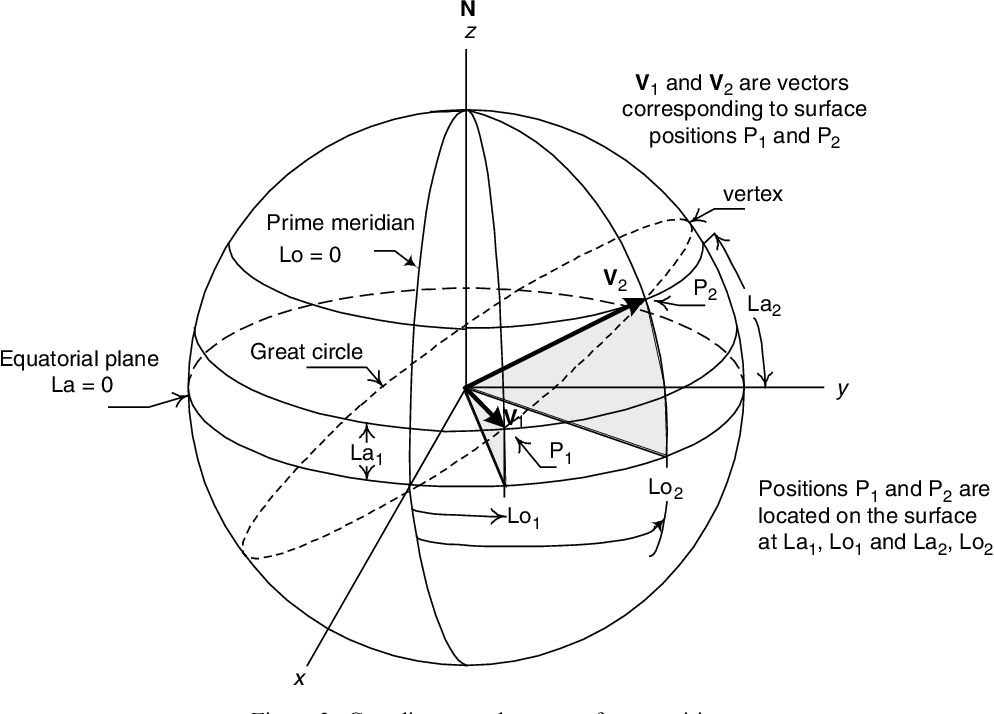
A Orthodrome is a navigational concept used in the field of navigation"
especially in maritime and aeronautical navigation. An orthodrome, also known as a great circle route or geodesic line, is the shortest path between two points on the surface of a sphere, such as the Earth. The term "orthodrome" comes from the Greek words "ortho," meaning straight, and "dromos," meaning course or path. These routes are of particular importance in navigation, aviation, and maritime activities because they represent the most efficient way to travel between two distant points on the Earth's surface.
Key characteristics of a Orthodrome include:
- Shortest Distance: An orthodrome represents the shortest distance between two points on the Earth's surface. It is the path that a plane or ship would take to cover the least amount of ground.
- Great Circle: Orthodromes are segments of great circles, which are the largest circles that can be drawn on a sphere. They are analogous to the equator on Earth.
- Varying Compass Bearings: While an orthodrome represents the shortest distance, the compass bearing or course along an orthodrome may vary as you progress along the route. Pilots and navigators need to constantly adjust their heading to stay on the great circle path.
- Polar Convergence: Orthodromes converge at the poles of the sphere. As you get closer to a pole, the path spirals inwards and ultimately meets at the pole.
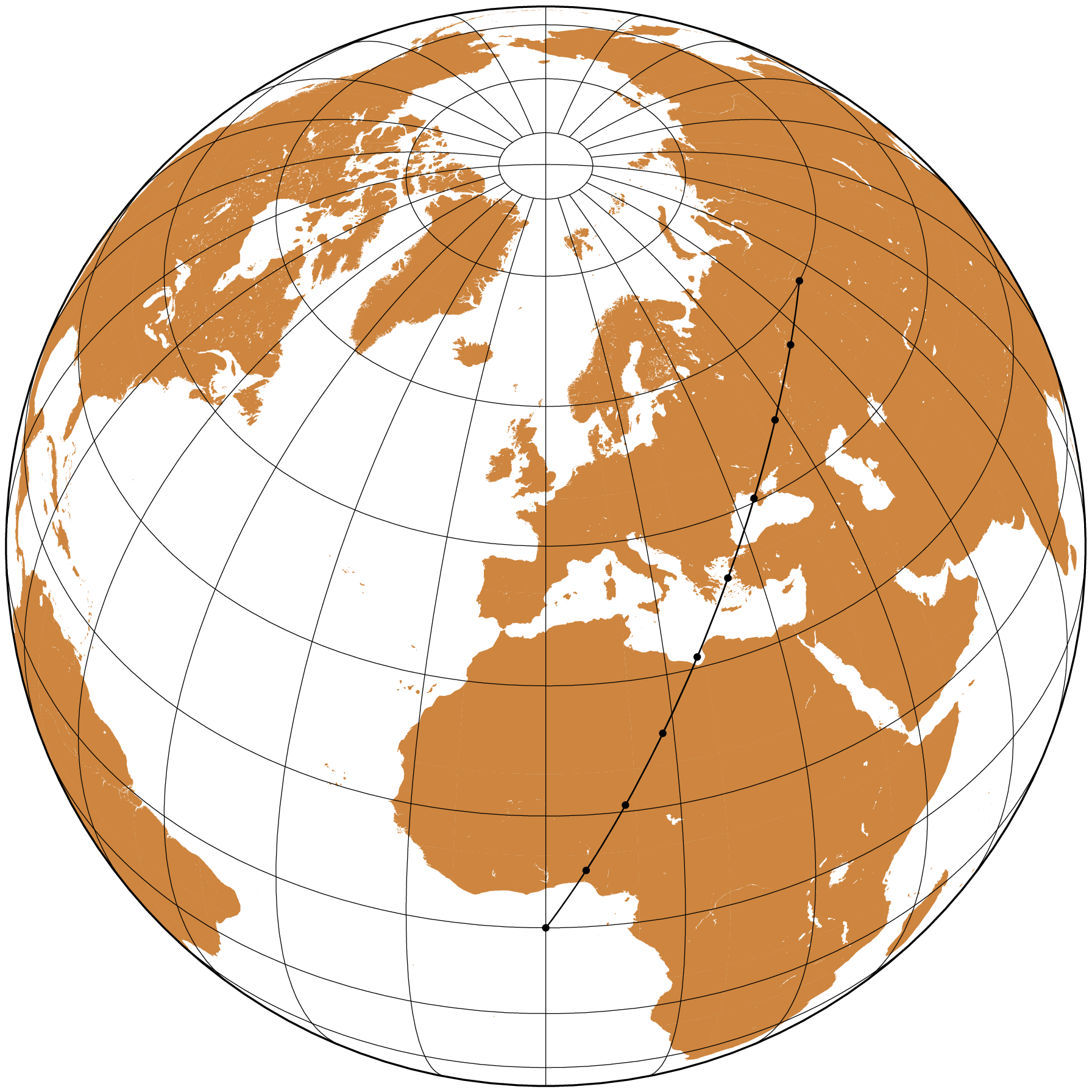
In summary
an orthodrome is the shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere, such as the Earth. It is a concept used in navigation to find the most efficient route for long-distance travel, taking into account the Earth's curved surface. Navigators and pilots use orthodromes to plan and follow the most direct path between two locations, which can be critical for fuel efficiency and time-saving in long journeys.
