Wind Triangle
The "wind triangle" is a fundamental concept in aviation that helps pilots calculate and compensate for the effects of wind on an aircraft's flight path. It is a graphical representation used to solve navigation problems involving airspeed, groundspeed, true heading, magnetic heading, and wind speed and direction. The wind triangle is a crucial tool for flight planning, navigation, and making in-flight adjustments to ensure safe and efficient flying.
Read MoreWind Triangle Calculator
NavigationTools.it is a specialized website designed to help aviation enthusiasts and pilots master wind triangle calculations. With educational resources the website aims to empower users in understanding and applying wind effects in aviation navigation.
Read More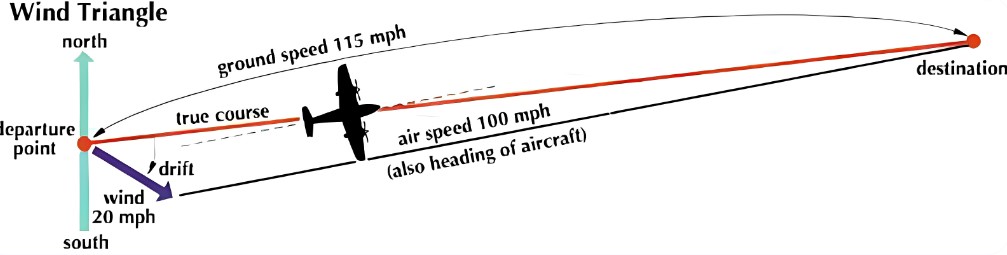
The wind triangle, also known as the "navigation triangle" or "air navigation triangle,"
is a fundamental concept in aviation used to calculate the effect of wind on an aircraft's course and groundspeed. It helps pilots determine the true heading they need to follow and their actual groundspeed when flying in the presence of wind. The wind triangle is a graphical representation that consists of three vectors: True Airspeed (TAS), Heading (HDG), and Wind (W). By using the wind triangle calculations, pilots can determine the heading they should fly (True Heading) and the actual groundspeed they will achieve in the presence of wind. This information is crucial for flight planning, navigation, and ensuring that the aircraft arrives at its destination on time and on course.
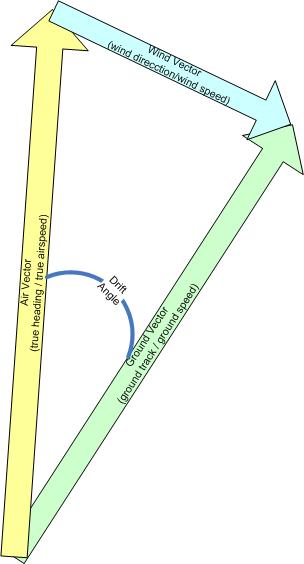
The key components of a wind triangle include:
- True Airspeed (TAS): This is the actual speed of the aircraft through the air, corrected for temperature and pressure at altitude. TAS is typically measured in knots.
- Groundspeed (GS): Groundspeed is the speed of the aircraft over the ground. It takes into account the aircraft's true airspeed and the effect of the wind. Groundspeed is also measured in knots and is the actual speed at which the aircraft is progressing along its flight path.
- True Heading (TH): True heading is the direction the aircraft is pointing concerning true north. It is measured in degrees true and is not affected by wind.
- Wind Speed and Direction: The wind's speed and direction are essential factors in the wind triangle. Wind speed is measured in knots, and wind direction is expressed in degrees
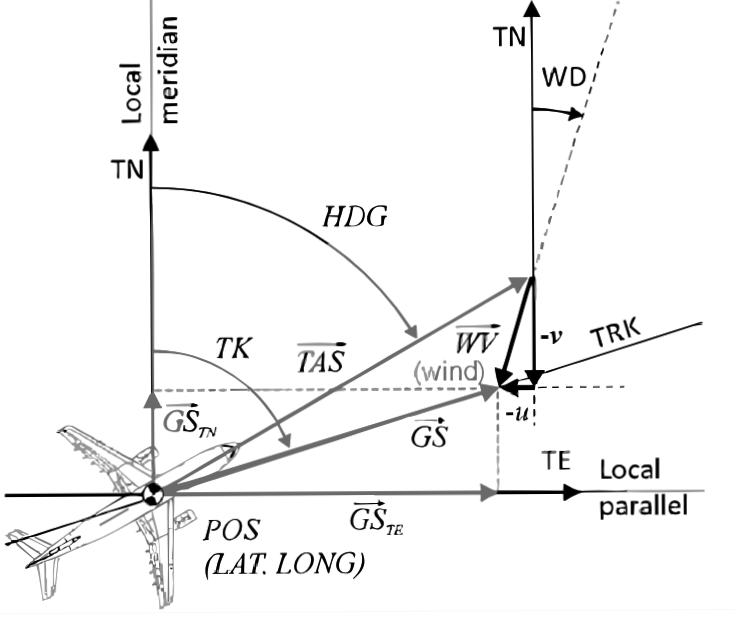
To calculate these values using the wind triangle, pilots use a navigation computer, electronic flight computer, or manual flight planning tools.
By inputting known values such as TAS, magnetic heading, and the wind information, pilots can solve for the missing components like TAS, GS, or true heading. This information is critical for planning flight routes, determining estimated time of arrival, and making in-flight adjustments to ensure the aircraft stays on course and arrives safely at its destination.
In summary, the wind triangle is a graphical tool used by pilots to account for the effects of wind on aircraft performance and navigation, helping them make accurate flight calculations and adjustments.
